The business landscape has become increasingly treacherous for companies of all sizes. Understanding how to mitigate cyber risk isn’t just good practice anymore—it’s essential for survival.
Based on what we’ve learned working with hundreds of businesses, there are several foundational steps that make the biggest difference in reducing your exposure to cyber threats.
A comprehensive risk assessment should always be your starting point. You can’t protect what you don’t know exists, so identifying your vulnerabilities gives you a clear roadmap for what needs attention first. From there, implementing multi-factor authentication across your critical systems creates an immediate security boost with relatively little effort.
Keeping your systems and software updated might sound basic, but you’d be surprised how many breaches happen through known vulnerabilities that simply weren’t patched. Setting up automated updates removes the human element from this critical protection.
Your team members can be either your greatest vulnerability or your strongest defense. Training employees to recognize phishing attempts and other social engineering tactics transforms them from potential security holes into an alert human firewall.
Network security becomes much more manageable when you establish proper access controls and segmentation. Not everyone needs access to everything, and compartmentalizing your network means a breach in one area won’t necessarily compromise your entire operation.
When disaster strikes—and unfortunately, it’s often a matter of “when” not “if”—having encrypted, off-site backups that you regularly test can be the difference between a minor inconvenience and a business-ending catastrophe. Pair this with robust endpoint protection that uses behavioral monitoring to catch what traditional antivirus might miss, and you’ve significantly improved your security posture.
Finally, having a well-documented incident response plan that you actually practice ensures everyone knows their role when seconds count.
The stakes couldn’t be higher. Cybersecurity breaches are projected to exceed 20 million annually by 2025, and the aftermath is often devastating—approximately 60% of small businesses close their doors within six months of experiencing a cyber breach.
The good news? You don’t need the budget of a Fortune 500 company to protect your business effectively. What matters more is a thoughtful, layered approach to security that addresses your specific risks.
The statistics paint a concerning picture: the average company now shares confidential information with 583 third parties, while over 3.4 billion phishing emails circulate globally every day. More than 80% of organizational data breaches can be traced back to weak passwords, and 94% of organizations have experienced security threats from within.
But here’s the silver lining: implementing the right security measures doesn’t just protect your business—it can actually improve productivity and compliance. With a structured approach to cyber risk mitigation, you can dramatically reduce your exposure while maintaining operational efficiency.
What is a Cyber Risk & Why Mitigation Matters
Let’s face it—the digital world can be a dangerous place for your business. But understanding cyber risk isn’t just about recognizing dangers; it’s about knowing exactly what you’re up against.
Cyber risk boils down to a simple equation: threats + vulnerabilities + potential impact = your risk level. Think of it as the perfect storm that could damage your business if left unaddressed.
A threat is anything that could potentially harm your organization—from sophisticated hackers and ransomware gangs to well-meaning employees who click on the wrong email link. These threats are constantly evolving, becoming more sophisticated by the day.
A vulnerability is essentially a weakness in your defenses. This could be outdated software, poorly configured cloud services, or even gaps in your security awareness training. Every organization has vulnerabilities—the key is finding them before the bad guys do.
The consequences of a cyber incident can be devastating. Beyond the immediate financial impact, you might face lasting reputational damage, operational downtime, and even regulatory penalties that can haunt your business for years.
Here’s a sobering thought: according to the Ponemon Institute, the average company shares confidential information with 583 third parties. That’s 583 potential weak links in your security chain! Your digital ecosystem has grown more complex, and with it, your attack surface has expanded dramatically.
We’ve helped countless Austin-area businesses understand their unique risk profiles through our comprehensive Cybersecurity Risk Assessments. Time and again, we’ve seen the surprise on clients’ faces when they realize just how exposed they’ve been all along.
Common Cyber Risks Organizations Face
The threat landscape is vast, but certain risks consistently top the charts for businesses of all sizes:

Ransomware has become the nightmare scenario for many businesses. These attacks lock up your critical data and demand payment for its return. What’s particularly alarming is that 82% of ransomware incidents target companies with fewer than 1,000 employees—the very businesses that often lack robust security resources.
Phishing and Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks continue to evolve in sophistication. These deceptive tactics trick employees into revealing sensitive information or authorizing fraudulent wire transfers. The damage? Up to $2.9 billion in annual losses across businesses worldwide.
Malware remains a persistent threat, with approximately 18% of cyberattacks on small businesses attributed to these malicious programs. From keyloggers that steal passwords to trojans that create backdoors into your network, malware comes in countless forms.
DDoS attacks can bring your online operations to a screeching halt by flooding your systems with traffic. Unlike some threats that target specific industries, these equal-opportunity attackers can impact businesses of any size or sector.
IoT vulnerabilities create new entry points into your network. Those “smart” devices throughout your office? Each one potentially represents an open uped door if not properly secured.
Cloud misconfigurations have become increasingly common as businesses rush to adopt cloud services without proper security planning. A single misconfigured setting can expose sensitive data to the entire internet.
Weak authentication continues to be the low-hanging fruit for attackers. Over 80% of organizational data breaches involve poor password practices or lack of multi-factor authentication—essentially leaving your front door open uped.
Insider threats, whether malicious or accidental, remain a significant concern. Approximately 94% of organizations have suffered security incidents due to actions taken by their own employees or contractors.
Why Mitigation Differs From Risk Management
While people often use the terms interchangeably, cyber risk management and cyber risk mitigation play distinct roles in your security strategy—and understanding the difference is crucial.
Cyber risk management is the comprehensive approach that includes identifying, analyzing, evaluating, and addressing all cybersecurity threats across your organization. It’s your big-picture strategy that guides everything else.
Cyber risk mitigation, on the other hand, is the specific actions, technologies, and procedures you implement to reduce both the likelihood and impact of cyber threats. Think of it as the hands-on part of your security program.
When tackling cyber risk, you have four main response options in your toolkit:
Risk mitigation involves implementing controls to reduce risk—like deploying multi-factor authentication or training your staff on security awareness. This is typically your front-line defense.
Risk avoidance means eliminating certain activities altogether. For example, you might decide not to collect certain customer data if the security risks outweigh the business benefits.
Risk transfer shifts some financial burden to a third party, usually through cyber insurance. While insurance won’t prevent an attack, it can help you recover financially afterward.
Risk acceptance comes into play when you’ve analyzed a risk and decided that the cost of mitigation exceeds the potential impact. This should be a conscious, documented decision—not the result of overlooking threats.
Most effective security programs use a blend of these approaches. The key is making informed decisions about which risks to mitigate and how, based on your specific business needs and resources.
The NIST Special Publication 800-30 provides an excellent framework for assessing risks and determining your mitigation priorities. This methodical approach ensures you’re focusing your efforts (and budget) where they’ll have the greatest impact on reducing your overall cyber risk.
Mitigating cyber risk isn’t a one-size-fits-all proposition. Your strategy should be as unique as your business.
How to Mitigate Cyber Risk: The 5-Layer Strategy
Picture cybersecurity as layers of an onion—each one providing additional protection for your valuable digital assets. This isn’t just IT jargon; it’s a practical approach we’ve seen work for real businesses time and again.
At Stradiant, we’ve helped countless businesses across Central Texas build these protective layers. What we’ve found is that a systematic, defense-in-depth strategy gives you the best shot at keeping the bad guys out—or containing them quickly if they do get in.
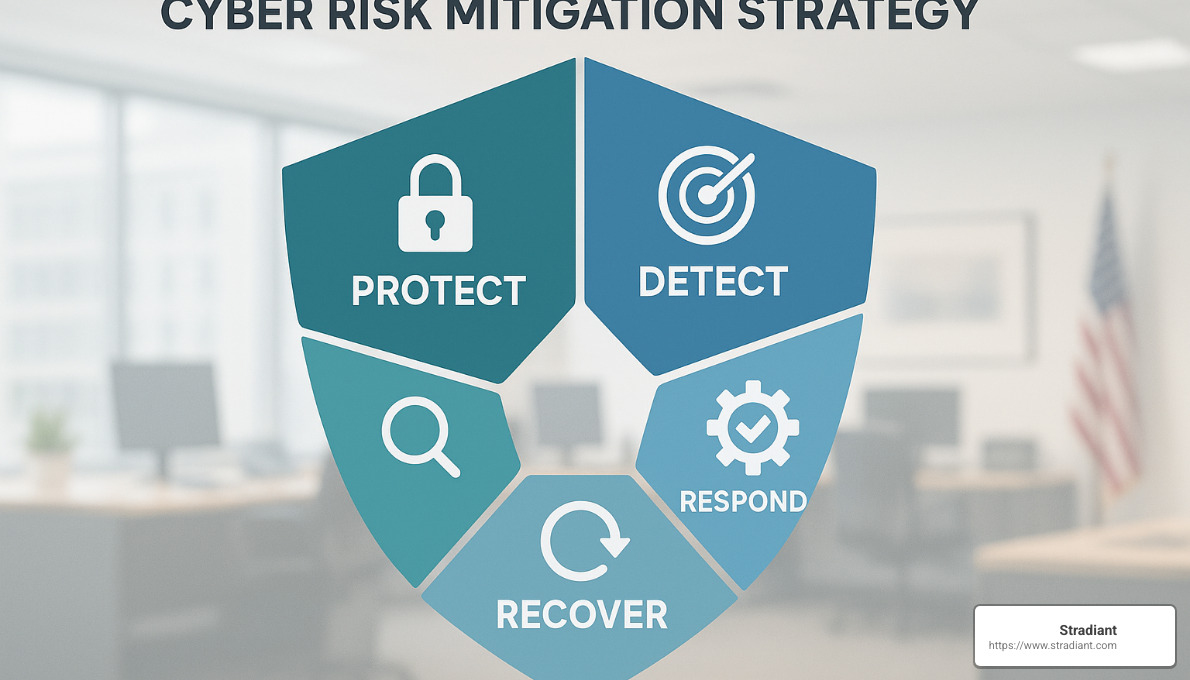
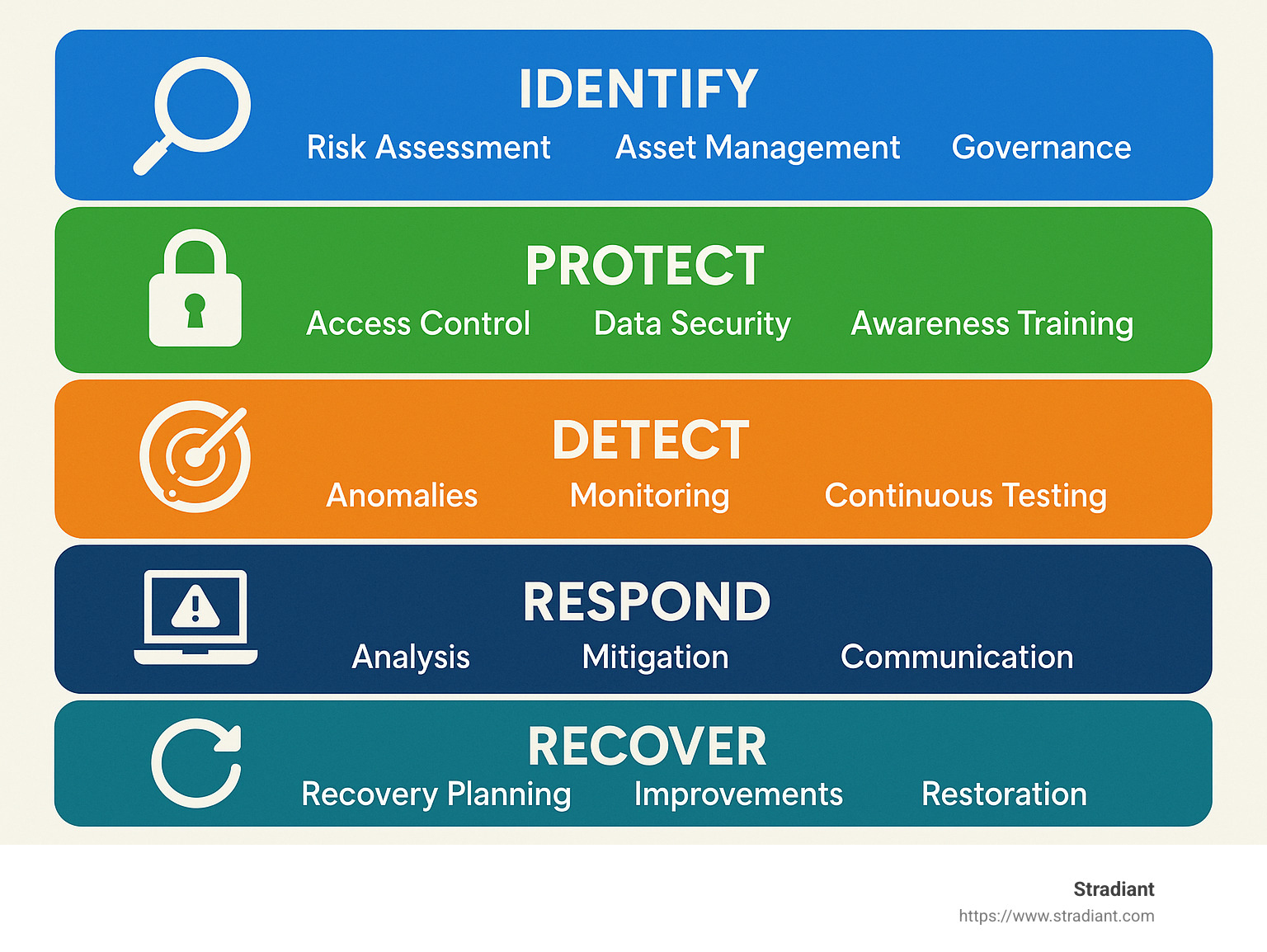
The backbone of our approach is the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF), which breaks down cybersecurity into five essential functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. This framework isn’t just theoretical—it’s a battle-tested roadmap used by organizations worldwide.
For the technically-minded, the NIST Risk Management Framework provides a structured process for implementing security controls. If you’re looking at global standards, ISO 27001 offers an internationally recognized approach that many partners and clients might recognize.
Now, let’s break down each layer of this strategy in ways that make practical sense for your business:
How to Mitigate Cyber Risk Layer 1 – Identify & Prioritize Assets
You can’t protect what you don’t know you have. It sounds obvious, but you’d be surprised how many businesses have forgotten systems or “shadow IT” lurking in their environment.
Start with a thorough asset inventory. This means documenting every piece of hardware, software, data repository, and system in your environment. We recently helped a South Congress retailer find three forgotten servers still running in their environment—all unpatched for years and prime targets for attackers.
Next, implement data classification. Not all information is created equal. Your customer database needs more protection than the lunch menu. By categorizing your data based on sensitivity and value, you’ll know where to focus your efforts.
Conduct a business impact analysis to understand what’s truly at stake. Ask yourself: “If this system went down or this data was stolen, what would happen to our business?” Consider financial losses, operational disruptions, regulatory penalties, and damage to your reputation.
Finally, map your attack surface—all the ways someone could potentially get into your systems. This includes internet-facing services, remote access points, physical locations, and connections to vendors or partners.
One healthcare provider we work with in Austin finded through this process that they had nearly a third more connected devices than they thought—including medical equipment with default passwords still enabled. Yikes!
Pro tip: Start with your crown jewels—the systems and data that would shut down your business if compromised—and work outward from there.
How to Mitigate Cyber Risk Layer 2 – Protect with Preventive Controls
Once you know what needs protecting, it’s time to build your defensive walls. This layer is all about making it harder for attackers to succeed.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is your best friend here. By requiring something you know (password) and something you have (like a phone app), you can block 99.9% of account compromise attempts. We make this a non-negotiable for all our clients, especially for access to email, VPNs, and admin accounts.
Encryption ensures that even if data is stolen, it remains unreadable without the encryption keys. Think of it as sending messages in a secret code that only authorized people can decipher. This applies both to data sitting on your systems and information traveling across networks.
The zero trust approach flips traditional security on its head. Instead of trusting everything inside your network, zero trust assumes potential threats everywhere and requires continuous verification. As we like to tell our clients in Round Rock: “Trust no one, verify everything.”
Patch management might not be exciting, but it’s essential. Most successful attacks exploit known vulnerabilities that could have been patched. For our clients in Kyle and Buda, we typically aim to patch critical vulnerabilities within 24-48 hours of release—before attackers can take advantage.
A manufacturing client implemented these controls under our guidance and saw security incidents drop by 75% in just three months—even as cyber attacks against their industry were increasing.
Budget-friendly tip: If resources are tight, focus first on implementing MFA and establishing a regular patching schedule. These two controls alone will dramatically reduce your risk exposure without breaking the bank.
Detect Layer – Continuous Monitoring & Threat Hunting
Even with strong defenses, some threats will slip through. The detect layer is about catching them quickly before they can do serious damage.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools go beyond traditional antivirus by monitoring for suspicious behaviors on devices. They’re like having a security guard watching each computer for unusual activity, rather than just checking IDs at the door.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems collect logs from across your environment and help identify patterns that might indicate an attack. For a small business, this might seem overwhelming, but even basic centralized logging can make a huge difference.
Anomaly detection establishes what “normal” looks like in your environment, then flags deviations. For example, if an employee suddenly logs in from overseas at 3 AM when they’ve never done so before, that’s worth investigating.
Threat hunting takes a proactive approach by assuming attackers may already be in your network and actively searching for signs of their presence. It’s like regularly checking all the rooms in your house, not just waiting for the alarm to go off.
With approximately 2,200 cyber attacks occurring daily (that’s one every 39 seconds), detection capabilities aren’t optional luxuries—they’re necessities.
Starting point: Begin with centralized logging of your most critical systems and gradually expand. Even basic anomaly detection can catch many common attack patterns.
Respond Layer – Build & Test an Incident Response Plan
When (not if) a security incident occurs, how you respond makes all the difference. This layer focuses on containing the damage and getting back to business quickly.
Your Incident Response Plan (IRP) is the playbook your team will follow during a crisis. It should clearly outline who does what, communication protocols, and decision-making authority. We’ve seen too many businesses waste precious hours during an attack simply trying to figure out who’s in charge.
Build a response team with representatives from different departments—IT, security, legal, communications, and leadership. Cybersecurity incidents aren’t just technical problems; they’re business problems that require coordination across the organization.
Tabletop exercises are like fire drills for cyber incidents. Regularly simulating different scenarios helps your team practice their response without the pressure of an actual attack. One financial services client in Bee Cave conducts quarterly exercises and was able to contain a ransomware attack before it spread beyond a single department—saving potentially hundreds of thousands in recovery costs.
Develop containment strategies in advance so you’re not making critical decisions under pressure. Having pre-approved procedures for isolating affected systems prevents attackers from moving laterally through your network.
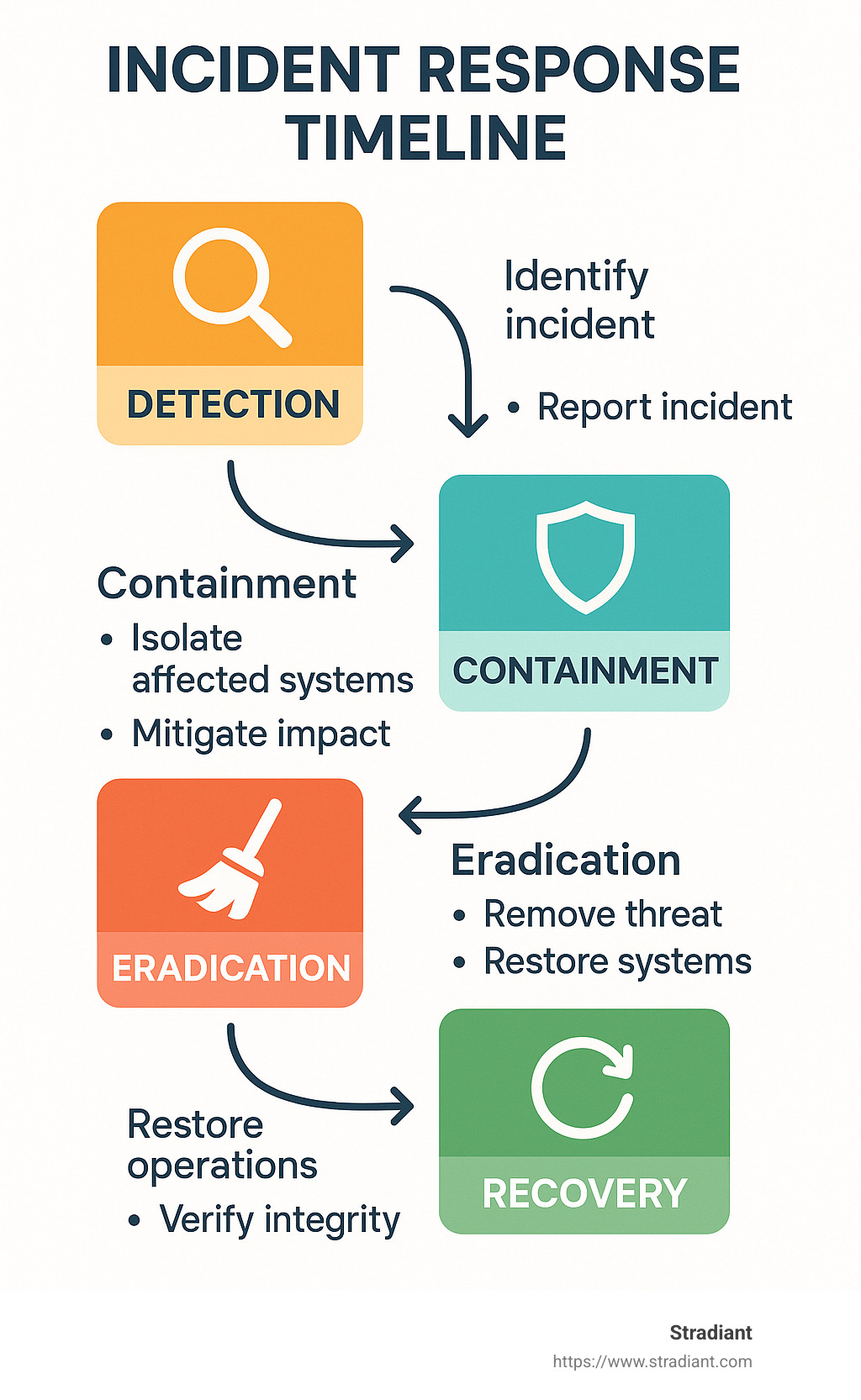
Recover Layer – Backup, BCP & Cyber Insurance
The final layer addresses how your business returns to normal operations after an incident and manages the financial impact.
A solid backup strategy follows the 3-2-1 rule: three copies of your data, on two different media types, with one copy stored off-site. But here’s the critical part many miss: regularly testing your restores. We’ve seen businesses with perfect backup schedules find during a crisis that their backups were corrupted or incomplete.
Business Continuity Planning (BCP) goes beyond technical recovery to address how your business functions during disruption. Which processes are critical? What’s your communication plan? How will you serve customers if systems are down? For our clients in Lakeway and Lost Creek, we recommend testing these procedures at least quarterly.
Disaster Recovery plans provide the technical roadmap for restoring systems after an incident. These should include detailed, step-by-step procedures that could be followed even by someone unfamiliar with your environment (because your key IT person might be unavailable during a crisis).
Cyber Insurance has become essential for managing financial risk. However, be aware that insurers are increasingly requiring specific security controls before providing coverage. We help our clients understand these requirements and implement the necessary measures to qualify for better coverage at lower premiums.
Practical tip: Ensure your backups are not only regular but also protected from ransomware. Modern attacks specifically target backup systems, so immutable backups or offline copies are essential for true recovery capability.
Technical and Process Controls You Can’t Ignore
Let’s face it – cybersecurity can feel overwhelming with so many moving parts. But after helping hundreds of businesses across Central Texas, we’ve identified the technical controls that give you the biggest bang for your buck. These aren’t just nice-to-haves; they’re the foundation of effective cybersecurity strategies.
Think of these controls as your digital security guards – they work 24/7 to keep the bad guys out while letting legitimate business continue without disruption.
Next-Generation Firewalls do far more than their older counterparts, inspecting even encrypted traffic to spot threats hiding in what looks like normal communication.
Network Segmentation works like fireproof doors in a building – even if one area catches fire, it doesn’t spread everywhere. We helped a manufacturing firm in Round Rock implement this approach, and when they experienced a ransomware incident, it affected only one department instead of their entire operation.
Privileged Access Management is crucial because administrator accounts are like master keys to your kingdom. When these fall into the wrong hands, the damage can be catastrophic. We recommend treating these accounts like the crown jewels – protected, monitored, and used only when absolutely necessary.
Signed Code Execution policies ensure only trusted software runs in your environment, while Secure Boot leverages hardware-level security to prevent tampering with the startup process – think of it as making sure no one messes with your car before you get in.
Advanced Endpoint Protection like endpoint detection and response (EDR) has become essential as remote work expands. These tools don’t just block known threats; they watch for suspicious behavior and can automatically contain problems before they spread.
For cloud environments, Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) continuously monitors for misconfigurations – the digital equivalent of making sure all your windows and doors are properly locked.
Reducing the Attack Surface & Managing Vulnerabilities
Imagine your business as a house. Every door, window, vent, and pipe represents a potential entry point for intruders. The more entry points you have, the harder they are to protect. That’s your attack surface, and reducing it is one of the smartest ways to mitigate cyber risk.
Asset Removal might sound obvious, but you’d be surprised how many unnecessary systems accumulate over time. We recently helped a client find they were running 17 services that nobody had used in over a year – each one a potential vulnerability. Removing these digital dust-collectors immediately strengthened their security posture.
Configuration Baselines establish the secure “normal” for your systems. Think of it as setting the rules for how your technology should behave – and making sure nothing deviates without good reason. When properly implemented, these baselines catch misconfigurations before they become problems.
Automated Patching is like having a team that constantly repairs tiny holes in your fence before they become big enough for intruders to slip through. One healthcare provider we work with reduced security incidents by 68% simply by implementing automated patching for critical systems.
Vulnerability Scanning works like a regular health check-up, identifying weak spots before they cause problems. We recommend quarterly scans at minimum, though many of our clients in higher-risk industries run them monthly or even weekly.
A small but mighty tip we share with all our clients: conduct a quarterly review of internet-facing services and remove any that aren’t actively needed. It’s like closing unnecessary doors and windows before a storm hits.
Automation & Modern Tech for Faster Mitigation
The cybersecurity landscape moves too quickly for purely manual approaches. Modern threats require modern solutions, and automation is your best friend when it comes to keeping pace.
AI-Driven Analytics can spot patterns that human analysts might miss, especially when dealing with massive amounts of data. One technology company in Pilot Knob implemented AI-based tools and caught a sophisticated attack that had been lurking undetected for weeks, quietly gathering data.
Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platforms turn hours of manual security work into automated workflows that happen in minutes or seconds. When a suspicious email arrives, these systems can automatically isolate it, analyze attachments, check sender reputation, and either quarantine or deliver it – all before a human would have finished their first cup of coffee.
Secure Score Monitoring tools like Microsoft Secure Score give you an at-a-glance view of your security posture and specific recommendations for improvement. One client described it as “having a security consultant who works 24/7 and never sends an invoice.”
Threat Intelligence Platforms connect you to the broader security community, giving you early warnings about emerging threats. It’s like having scouts who report back about danger before it reaches your doorstep.
Reputation Services check the digital “criminal records” of files, websites, and email senders before allowing them into your environment. These multi-layered checks happen in milliseconds but can prevent hours or days of cleanup after an infection.
If you’re just getting started with automation, begin with the basics – automated vulnerability scanning and patch deployment will give you immediate security benefits while you build familiarity with these technologies.
Human, Vendor & Compliance Safeguards
Technology alone isn’t enough to keep your business safe. The truth is, your people and processes are just as crucial to your cybersecurity strategy as any fancy software or hardware solution you might implement.

The Human Element: Security Awareness Training
Your team members can be either your greatest cybersecurity weakness or your strongest defense line. It’s a sobering thought that 68% of breaches involve non-malicious human error, according to Verizon’s research. That’s why we take employee training so seriously.
Our Cybersecurity Awareness Training programs for businesses focus on making security second nature to your staff. We don’t just lecture them—we engage them with regular simulated phishing exercises that help them spot suspicious emails before they click. We teach them to recognize various social engineering tactics that might target them both online and in person.
We also cover practical skills like safe data handling procedures for sensitive information and establish clear incident reporting processes so your team knows exactly what to do when something seems off.
Want to see immediate results? Try conducting monthly phishing simulations with your team. When someone falls for the test, provide immediate feedback and a quick training refresher. The improvement you’ll see month over month will surprise you.
Managing Third-Party & Supply-Chain Risk
Statistic about the average company sharing confidential information with 583 third parties? Each one of those relationships represents a potential back door into your systems. According to Verizon, about 15% of breaches involve a third party or supplier—people you’ve intentionally given access to your network.
The key is taking a structured approach to these relationships. Start with thorough vendor risk assessments before you sign any contracts. Don’t just take their word for it—really evaluate their security posture. Then implement continuous monitoring to make sure they maintain those standards over time.
Be specific about your security requirements in vendor contracts, so expectations are crystal clear. And always follow the principle of least privilege by providing vendors with only the minimum access necessary to do their jobs.
For businesses with limited resources, we recommend creating a tiered approach to vendor management. Focus your most rigorous assessments on the vendors that handle your most sensitive data or have direct access to your systems.
Ensuring Compliance While Mitigating Risk
Compliance and security should be partners, not competitors for your attention and resources. Many regulatory frameworks actually provide excellent foundations for building a solid security program.
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework offers a comprehensive approach to managing and reducing risk. The CIS Controls give you a prioritized set of actions to protect your organization from known attack vectors. And recent US cybersecurity regulations have established new requirements for data protection, regular audits, and incident response planning.
We help our clients build security programs that kill two birds with one stone—satisfying compliance requirements while actually improving security. For example, we helped a healthcare provider implement controls that both checked all the HIPAA requirement boxes and genuinely strengthened their security posture.
The NSA has published a list of recommendations and best practices that align with these frameworks and provide practical guidance for organizations of all sizes.
A practical tip: Try mapping your security controls to multiple compliance frameworks. This helps you identify gaps and avoid duplicating your efforts.
Building a Security-First Culture
The most powerful—and often overlooked—aspect of how to mitigate cyber risk is your company culture. When security becomes part of your organizational DNA, it transforms from an IT concern into everyone’s responsibility.
Building this culture starts at the top with strong executive buy-in. Your leadership team needs to visibly support and prioritize security initiatives. If the boss doesn’t care about security, why should anyone else?
Regular metrics sharing helps keep security top of mind. When you communicate security metrics and incidents to all employees, you reinforce that this is a shared responsibility.
Consider creating positive incentives for security-conscious behavior rather than just punishing mistakes. Reward the employee who reports a suspicious email or identifies a potential vulnerability. Celebrate these wins!
Security is a journey, not a destination. Continuous improvement should be your mantra. Treat security as an ongoing process that evolves with your business and the threat landscape.
Want to make an immediate impact? Include security considerations in performance reviews for all employees, not just IT staff. This signals that security is truly everyone’s job.
Frequently Asked Questions about How to Mitigate Cyber Risk
What is the first step when learning how to mitigate cyber risk?
You can’t protect what you don’t understand. That’s why the first step in any cyber risk mitigation journey is always a comprehensive risk assessment. Think of it as getting a complete physical – you need to know where you stand before you can improve.
A proper risk assessment involves taking inventory of your digital assets, understanding what threats are most likely to affect your business, evaluating how vulnerable you are to those threats, and determining what impact a successful attack would have on your operations. Once you have this information, you can prioritize your risks based on both likelihood and potential damage.
We begin every new client relationship with a thorough assessment. We’ve found that many Austin businesses are surprised by what we find – from forgotten servers running outdated software to critical business systems with default passwords still in place. This initial assessment establishes your security baseline and helps us identify where we can make the biggest impact right away.
Which technical control offers the biggest ROI?
If you’re looking for the biggest security bang for your buck, multi-factor authentication (MFA) is consistently the winner. It’s relatively inexpensive to implement but prevents the vast majority of account compromise attacks. In fact, Microsoft reports that MFA can block over 99.9% of account compromise attacks.
Other high-ROI controls that we often recommend include privileged access management to control who has administrative rights, robust email security with anti-phishing capabilities, regular and tested backups that can’t be reached by ransomware, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems that can spot and stop attacks in progress.
The beauty of these controls is that they don’t require enterprise-level budgets but provide substantial protection against the most common attack vectors. For small to medium businesses in Central Texas, these are often the perfect place to start.
How often should we review our cyber-risk mitigation plan?
Cybersecurity isn’t a “set it and forget it” proposition – it’s more like gardening than building a fence. You need regular attention and maintenance to keep things healthy.
We recommend treating cyber risk mitigation as a continuous process with several review cycles:
First, continuous monitoring should be happening all the time – your systems should be constantly checking for suspicious activities and alerting you to potential problems.
Quarterly, you should take a step back and review your overall security posture and incident response plans. This is a good time to ask: “Are our current controls still working? Have our risks changed? Are our response plans still relevant?”
Annually, conduct a comprehensive assessment of your entire cybersecurity program. This deeper dive helps identify gaps that might have developed over time and ensures you’re keeping pace with evolving threats.
And of course, any significant change to your IT environment – like moving to a new cloud provider or implementing a major new system – should trigger an immediate review of your security controls.
For most of our clients throughout Austin and the surrounding communities, we provide monthly security reviews as part of our managed services. These regular check-ins help us spot potential issues before they become problems and ensure that your security posture stays strong even as your business evolves.
Measuring Success in Cyber Risk Mitigation
The journey of how to mitigate cyber risk is never truly complete. Rather than chasing the impossible goal of eliminating all risk, successful organizations focus on reducing risks to acceptable levels while preparing for the inevitable incidents that will occur.
Think of cyber risk mitigation as an ongoing health regimen rather than a one-time cure. Just as you wouldn’t measure your health by a single doctor’s visit, you need ongoing metrics to gauge your cybersecurity health.
At Stradiant, we’ve found that businesses thrive when they track these key performance indicators:
Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) shows how quickly your team identifies potential security incidents. When we helped a manufacturing client in South Austin reduce their MTTD from days to hours, they prevented what could have been a catastrophic breach.
Mean Time to Respond (MTTR) measures your response speed once threats are detected. One of our financial services clients in Lakeway slashed their MTTR by 60% after implementing our recommended incident response procedures.
Security Control Coverage tells you what percentage of your environment is protected by essential security measures. Are there gaps in your armor? This metric helps you find them.
Vulnerability Remediation Time tracks how quickly you address known weaknesses. In today’s threat landscape, leaving vulnerabilities unpatched is like leaving your doors open uped in a high-crime neighborhood.
Security Training Completion Rates measure your human firewall’s strength. Your team can be either your greatest vulnerability or your strongest defense.
Incident Frequency and Severity show the real-world impact of your security program. When these numbers decrease over time, you know you’re on the right track.
Your approach to how to mitigate cyber risk should be as unique as your business. The cookie-cutter solutions that dominated cybersecurity in the past simply don’t work today. Your industry, size, data sensitivity, compliance requirements, and risk tolerance all shape what an effective strategy looks like for you.
By implementing the layered strategy we’ve outlined and committing to continuous measurement and improvement, you can dramatically reduce your exposure to cyber threats without breaking the bank—or your sanity.
You don’t have to steer these waters alone. Our team is available around the clock to help businesses throughout Central Texas develop and implement effective strategies custom to their specific needs.
For more information about our comprehensive approach to protecting your business, visit our cyber-security page or reach out today to schedule a risk assessment.
The digital landscape may be dangerous, but with the right approach to cyber risk mitigation, you can steer it confidently—without losing your mind or your data.

