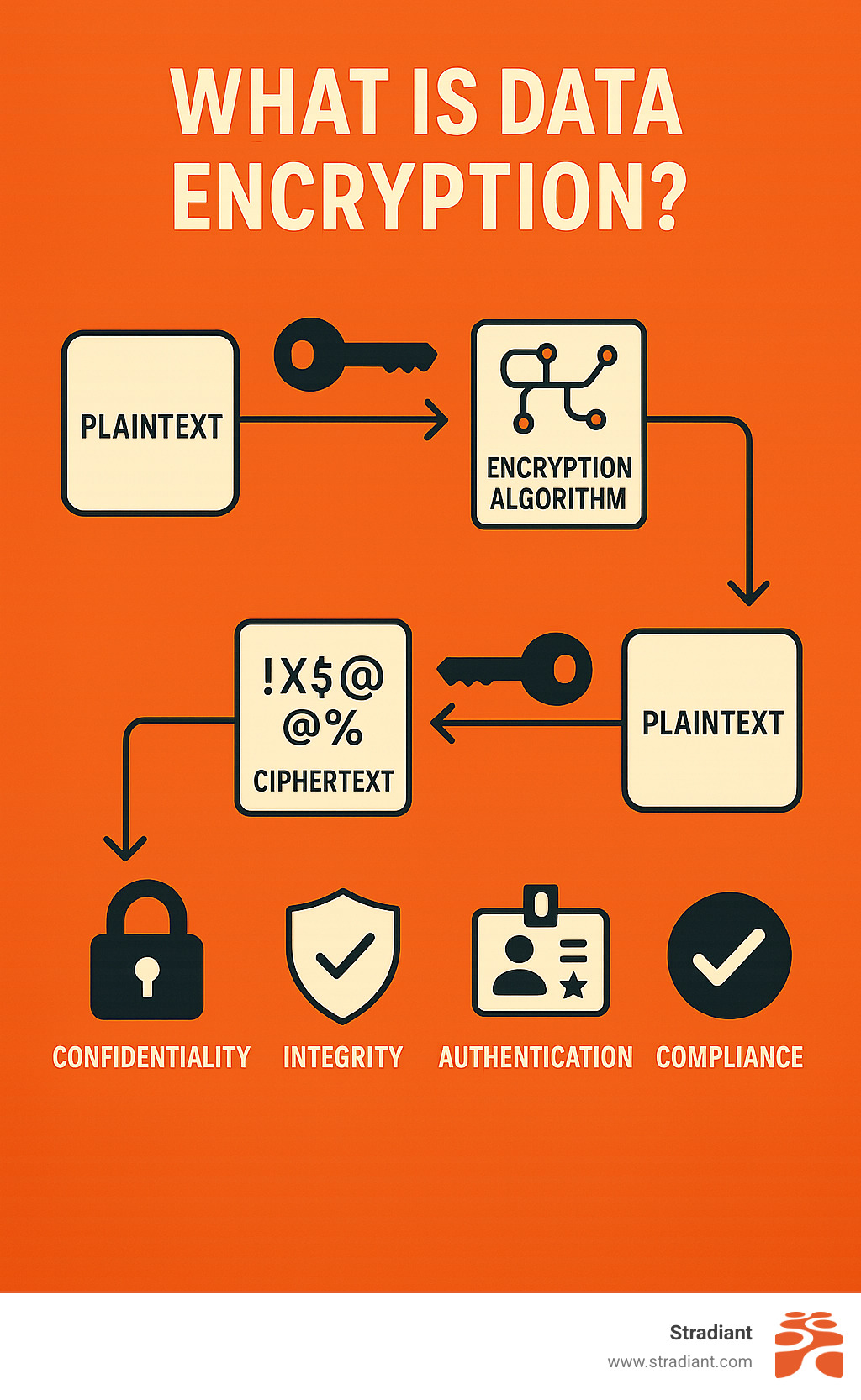
Data encryption is the process of converting readable information (plaintext) into scrambled, unreadable code (ciphertext) using mathematical algorithms and secret keys. Only authorized parties with the correct decryption key can restore the data to its original form.
Quick Answer: What is Data Encryption?
- Purpose: Blocks unauthorized access to sensitive data
- Process: Turns readable text into unreadable code with algorithms
- Key Required: Secret key needed to decrypt the information
- Benefits: Delivers confidentiality, integrity, and compliance
- Use Cases: Secures data at rest, in transit, and during processing
Every day your organization collects customer details, financial records, employee files, and trade secrets. Left unprotected, that information is an open invitation to cyber-criminals. The average cost to fix a breach reached $4.45 million in 2023—a number that can wipe out a small or medium-sized business. Companies already using encryption cut those losses by more than $220,000.
Good news: modern encryption tools work quietly in the background, so you gain security without slowing daily operations.
What Is Data Encryption? Core Concepts
When you encrypt data, you’re changing normal, readable information (we call this plaintext) into complete gibberish (called ciphertext) using complex mathematical formulas and a secret key. It’s like having the world’s most sophisticated secret decoder ring.
Here’s how it works in practice: Let’s say your plaintext message is “Our Q4 revenue increased 25%.” After encryption, it might look like “Rxu D4 uhyhqxh lqfuhdvhg 25%.” Pretty meaningless to anyone snooping around, right?
The magic happens with the encryption key – think of it as the combination to your digital safe. This string of characters tells the algorithm exactly how to scramble your data and, more importantly, how to unscramble it when you need it back.
Modern encryption delivers four essential security benefits that protect your business. Confidentiality ensures only the right people can read your sensitive information. Integrity lets you detect if someone has messed with your data. Authentication verifies who actually sent that important message. And non-repudiation means the sender can’t later claim they never sent it – crucial for business contracts and communications.
The scientific research on cryptography reveals just how powerful today’s encryption really is. We’re talking about mathematical problems so complex that even if every computer on Earth worked together, they’d need thousands of years to crack a single encrypted message through brute force.
What is Data Encryption vs Hashing?
Here’s where things get interesting – and where many business owners get confused. Encryption and hashing are like cousins in the cybersecurity family, but they have very different jobs.
Encryption is like a locked box with a key. You can always open it and get your original data back if you have the right key. This two-way process makes encryption perfect for protecting files, emails, and databases that you need to access regularly.
Hashing is more like a paper shredder that creates a unique fingerprint. Once you hash something, there’s no going back – it’s a one-way trip. Hash functions take your data and create a completely unique “digital fingerprint” or digest. Change even one letter in your original data, and the entire hash changes dramatically.
This makes hashing incredibly useful for integrity checks. When you download software updates, the company provides a hash of the original file. You can hash your downloaded copy and compare – if the hashes match, you know the file wasn’t corrupted or tampered with during download.
Your business benefits from both technologies working together. We hash your passwords so even we can’t see them, while we encrypt your customer databases so you can still access them securely. It’s like having both a safe and a security alarm – multiple layers of protection keep your business data bulletproof.
How Does Data Encryption Work
Imagine encryption as a sophisticated lock-and-key system, but instead of physical mechanisms, it uses mathematical wizardry to protect your data. The process might sound complex, but understanding the basics will help you make better security decisions for your business.
At its heart, encryption uses algorithms – step-by-step mathematical procedures that scramble your data in predictable but complex ways. These algorithms perform two main operations: substitution (swapping characters for other characters) and permutation (rearranging the order of characters).
Think of it like this: if you wanted to hide the word “PROFIT,” substitution might change it to “QSPGJU” (shifting each letter by one), while permutation might rearrange it to “FIPTOR.” Real encryption algorithms do both operations thousands of times in incredibly complex patterns.
The magic happens with key length – essentially, how long your secret password is. This isn’t just about having a longer password; it’s about exponential security. A 56-bit key gives you about 72 quadrillion possible combinations. Bump that up to 128-bit, and you’re looking at 340 undecillion combinations. With 256-bit encryption, you have more possible keys than there are atoms in the observable universe.
But length isn’t everything. The randomness and entropy of your encryption key matter just as much. A truly random key is like having a combination lock where every number was chosen by rolling dice, while a predictable key is like using your birthday as your password.
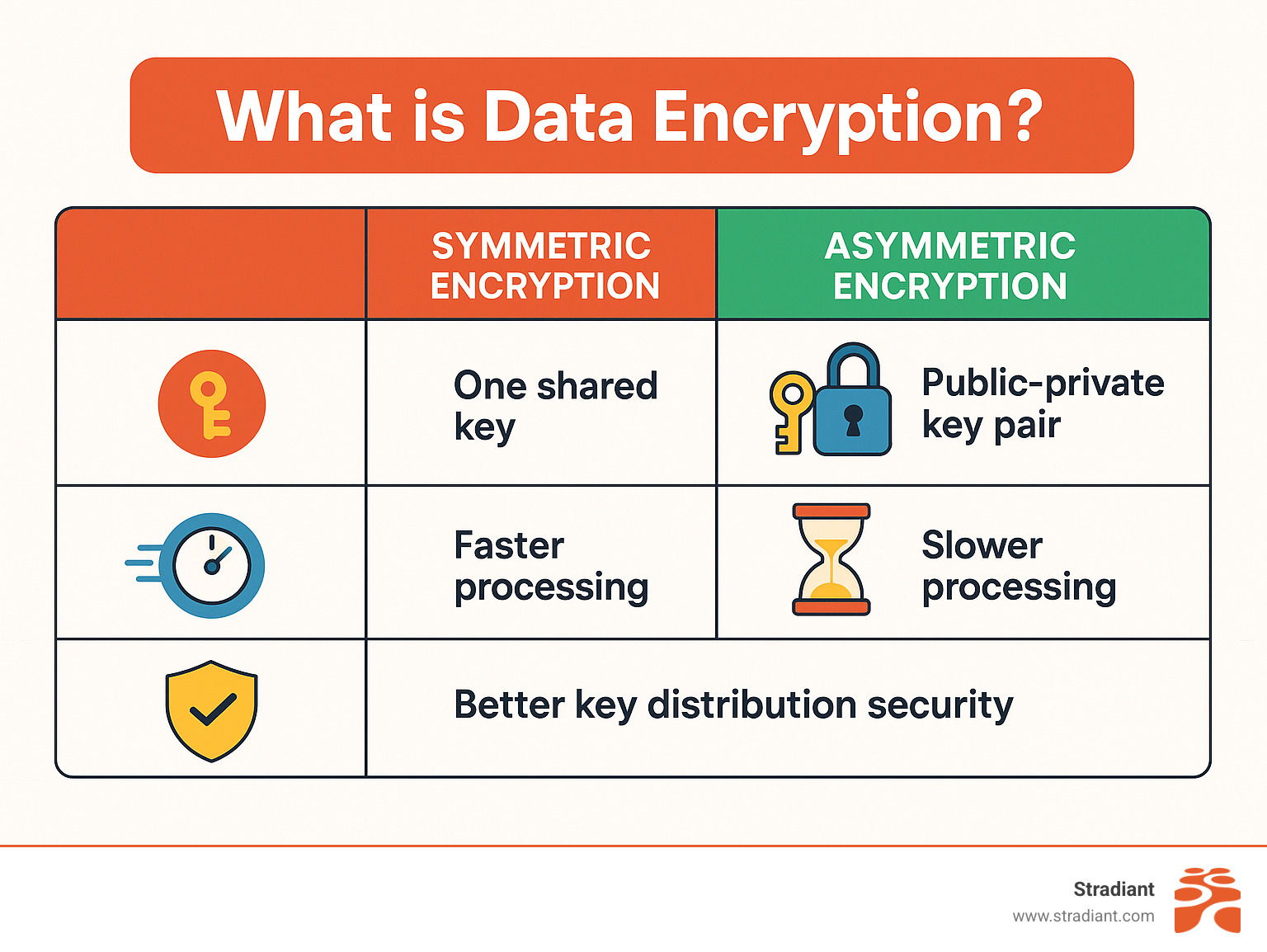
The table above shows the fundamental difference between symmetric encryption (one shared key for everything) and asymmetric encryption (separate public and private keys). Symmetric is faster and simpler – perfect for encrypting large amounts of data. Asymmetric is slower but solves the tricky problem of how to share keys securely with people you’ve never met.
What is Data Encryption in the Cloud?
Cloud encryption gets interesting because your data takes a journey – from your device, across the internet, and onto servers you’ll never see. Each step of that journey needs protection, and that’s where multiple encryption layers come into play.
Transport Layer Security (TLS) acts like an armored car for your data as it travels online. You see TLS working every time you notice that little lock icon next to a website address. It creates an encrypted tunnel between your browser and the website, so even if someone intercepts your data, they can’t read it.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) take this concept further by creating encrypted tunnels for all your internet traffic. Instead of just protecting individual website connections, a VPN encrypts everything – your emails, file uploads, video calls, the works.
The gold standard is end-to-end encryption. This means your data gets encrypted on your device before it even starts its journey, stays encrypted while traveling through the internet, and only gets decrypted when it reaches its final destination. It’s like putting your data in a locked box that only the intended recipient can open.
What is data encryption in the cloud becomes especially critical when you consider that your business data might pass through dozens of servers and network devices on its way to its destination. Each point in that journey is a potential vulnerability without proper encryption.
Types & Algorithms: From AES to Quantum-Safe

When people ask what is data encryption, they’re often surprised to learn there isn’t just one type. Think of encryption algorithms like different locks for different doors – each designed for specific security needs and situations.
The encryption world splits into two main camps: symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption. Symmetric encryption is like having one key that both locks and open ups your front door. It’s incredibly fast and perfect for protecting large files, but you face the tricky problem of safely getting that key to everyone who needs it.
Asymmetric encryption solves this puzzle by giving you two mathematically connected keys – one you can share publicly, and one you keep completely private. It’s like having a mailbox where anyone can drop off messages using your public slot, but only you have the private key to open it and read them. The trade-off? It’s much slower than symmetric encryption.
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) has become the heavyweight champion of symmetric encryption. The U.S. government trusts it with classified information, and it comes in three strengths: 128-bit, 192-bit, and 256-bit keys. Even with today’s most powerful computers, cracking AES-256 would take longer than the age of the universe.
For asymmetric encryption, RSA has been the reliable workhorse for decades. Named after its brilliant inventors Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman, RSA typically uses 2048 or 4096-bit keys. While it’s slower than AES, it’s perfect for encrypting small but critical pieces of data like passwords or the AES keys themselves.
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) brings efficiency to the asymmetric world. A 256-bit ECC key provides the same security as a massive 3072-bit RSA key, making it ideal for smartphones and other devices where processing power and battery life matter.
Twofish deserves mention as one of the fastest symmetric algorithms available, supporting key lengths up to 256 bits. Meanwhile, the old Data Encryption Standard (DES) has been officially retired – its 56-bit keys simply can’t stand up to modern computing power.
The history of cryptography reveals fascinating evolution from ancient Caesar ciphers to today’s quantum-resistant algorithms. We’re now preparing for a future where quantum computers might crack today’s RSA and ECC encryption by solving their underlying mathematical puzzles in minutes rather than millennia.
Post-quantum cryptography isn’t science fiction anymore. The National Institute of Standards and Technology is actively standardizing new algorithms designed to withstand quantum computer attacks. Homomorphic encryption represents another exciting frontier, allowing calculations on encrypted data without ever decrypting it – imagine analyzing customer trends while keeping individual data completely private.
What is Data Encryption for Small Business IT?
Small and medium businesses need enterprise-level protection without enterprise-level headaches. The good news? Modern encryption tools have become surprisingly user-friendly and affordable.
Device encryption should be your starting point. Full-disk encryption on every laptop, desktop, and mobile device means that even if equipment gets lost or stolen, your data stays locked away from prying eyes. Most modern operating systems include this feature – it just needs to be turned on.
Email encryption protects your daily communications automatically. Smart email systems can detect when you’re sending sensitive information like customer data or financial details and encrypt those messages without you having to think about it.
File-level encryption gives you surgical precision, letting you protect specific folders containing your most sensitive business information while leaving everyday files easily accessible.
Understanding what is data encryption and how to implement it properly doesn’t have to overwhelm your team. Our cybersecurity awareness training helps your employees recognize when encryption matters most and use these tools confidently. After all, the most sophisticated encryption in the world won’t protect you if your team doesn’t know when and how to use it.
Benefits, Use Cases & Compliance
Understanding what is data encryption becomes crystal clear when you see how it transforms your business security posture. Think of encryption as your digital bodyguard – it’s working 24/7 to protect your most valuable assets, even when you’re not thinking about it.
Data at rest is all the information sitting quietly on your servers, hard drives, databases, and backup systems. It might seem safe just sitting there, but unencrypted data at rest is like leaving cash on your desk overnight. Full-disk encryption wraps everything on a device in a protective shell, while database encryption adds targeted protection to your most sensitive customer records and financial information.
Data in transit covers the constant stream of information flowing through your networks – every email sent, file shared, video call made, and web page loaded. Modern TLS/SSL encryption handles most web traffic automatically (that’s the little lock icon in your browser), but your internal communications and file sharing need additional layers of protection.
The newest frontier is data in processing – protecting information while your applications are actively using it. This is where cutting-edge technologies like homomorphic encryption are making breakthroughs, allowing you to analyze data without ever exposing it.
Let’s look at how this plays out in the real world. Whole-disk encryption on laptops means a stolen device becomes worthless to thieves – they can’t access any of your data. Encrypted email ensures your sensitive communications stay private, whether you’re discussing payroll details or sharing customer information with remote team members.
VPN-based encryption creates secure tunnels for employees accessing company applications from coffee shops or home offices. Database encryption protects customer records in sectors like healthcare and finance, where a single breach could mean millions in fines and lost trust.
The compliance benefits alone make encryption a no-brainer for many businesses. PCI DSS doesn’t just recommend encryption for payment card data – it requires it. HIPAA mandates encryption for electronic health records, and GDPR makes encryption essential for protecting personal data of European customers.
Here’s what really gets business owners’ attention: the bottom line impact. Organizations using encryption reduce their average breach costs by over $220,000. When you consider that the average data breach now costs $4.45 million, that encryption investment pays for itself many times over.
The trust factor is huge too. Customers are increasingly savvy about data protection. When they know you’re encrypting their information, they’re more likely to do business with you and share the sensitive details you need to serve them better.
At Stradiant, we’ve seen how proper encryption strategies protect our Austin-area clients from devastating breaches. Our data backups & data recovery services include encryption by default because we know that unprotected backup data is often the weakest link in an otherwise secure system.
Challenges and Future of Encryption
Even bullet-proof algorithms have weak spots. Knowing the main challenges helps you strengthen your defense.
- Brute-force attacks try every possible key, but 256-bit encryption creates more combinations than atoms in the observable universe—mathematically out of reach.
- Side-channel attacks focus on the system (power draw, timing, electromagnetic leaks) rather than the math. Well-designed hardware and software can block those cues.
- Cryptanalysis sometimes reveals shortcuts, which is why outdated ciphers like DES were retired. The crypto community continuously tests and replaces aging standards.
- Key management causes most real-world failures. Lose or leak a key and even perfect encryption crumbles.
- Quantum computing could eventually break RSA and ECC, but post-quantum algorithms are already being standardized to stay ahead of that curve.
Artificial intelligence, BYOK (Bring Your Own Key), crypto-shredding, and homomorphic encryption are shaping the next generation of protection, letting businesses analyze or erase data without ever exposing the raw content.
Key Management Essentials
Getting keys right is non-negotiable.
- Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) store keys in tamper-resistant hardware.
- Key rotation automatically changes keys on a schedule to limit damage if one is compromised.
- Separation of duties ensures no single person can access or modify keys alone.
- Automated lifecycle management creates, distributes, rotates, and retires keys without human error.
Our beginners guide to cybersecurity risk assessments evaluates current key practices and maps a path to airtight management.
Frequently Asked Questions about Data Encryption
How strong is 256-bit encryption?
What is data encryption with 256-bit keys? It’s essentially unbreakable with today’s technology – and that’s not marketing hype, that’s mathematical reality.
To understand just how strong 256-bit encryption is, let’s talk numbers. A 256-bit key creates 2^256 possible combinations – that’s a number with 77 digits. If you could somehow get every person on Earth to run a computer that tested a billion different keys every single second, you’d still need more time than the universe has existed to try all the possibilities.
Even the looming threat of quantum computers doesn’t change this picture much for properly implemented 256-bit symmetric encryption like AES-256. While quantum computers could potentially break RSA and ECC encryption, they’d still struggle with strong symmetric encryption.
The real world is even more secure than these theoretical numbers suggest. Attackers don’t need to find your exact key – they just need to find any key that works. But with 256-bit encryption, there’s essentially only one key that works out of those astronomical number of possibilities.
Can encrypted data be hacked without the key?
Here’s the honest answer: strong encryption algorithms like AES-256 can’t be broken through brute force, but that doesn’t mean your encrypted data is automatically safe.
Cybercriminals are clever – if they can’t break the lock, they’ll look for other ways in. They might steal your encryption keys through malware on your computer or by tricking employees into revealing passwords. They could exploit weaknesses in how the encryption is implemented rather than attacking the algorithm itself.
Key management systems are often the weak link. Your encryption might be bulletproof, but if the system storing your keys has vulnerabilities, attackers can steal the keys and open up everything.
Social engineering remains incredibly effective. Why spend years trying to crack encryption when you can call someone pretending to be from IT support and ask for their password?
This is why we always tell our clients that encryption is just one piece of your security puzzle. You need proper key management, employee training, and multiple layers of protection working together. The strongest encryption in the world won’t help if someone tricks your receptionist into revealing the password.
Does encryption slow down my business applications?
The short answer is: not really, if it’s done right.
Modern encryption has come a long way from the days when it would noticeably slow down your computer. Hardware-accelerated AES encryption typically adds less than 1% overhead to most business applications. Your employees probably won’t even notice it’s running.
The performance impact depends on several factors. Modern processors include built-in AES acceleration – special circuits designed specifically for encryption that make the process incredibly fast. Well-designed encryption software takes advantage of these features and runs very efficiently.
The type of encryption matters too. Symmetric encryption like AES is lightning-fast compared to asymmetric encryption like RSA. That’s why most systems use a hybrid approach – asymmetric encryption to securely share keys, then symmetric encryption for the actual data.
The amount of data you’re encrypting makes a difference. Encrypting a few emails or documents? You won’t notice any slowdown. Encrypting terabytes of video files? That’ll take some time, but it’s usually a one-time process.
We’ve implemented encryption for hundreds of Austin-area businesses, and performance complaints are extremely rare. When encryption is properly configured for your specific systems and needs, it runs invisibly in the background, protecting your data without getting in your way.
The bigger question isn’t whether encryption will slow you down – it’s whether you can afford not to have it. A data breach will slow down your business a lot more than encryption ever will.
Conclusion
Understanding what is data encryption isn’t just about staying current with technology trends – it’s about protecting the lifeblood of your business. Every email you send, every customer record you store, and every financial transaction you process creates valuable data that cybercriminals want to steal.
The statistics don’t lie. Data breaches cost businesses an average of $4.45 million, and that number keeps climbing. For small and medium-sized businesses, a single breach can mean the difference between thriving and closing your doors forever. But here’s the encouraging news: businesses that implement proper encryption reduce their breach costs by over $220,000.
Modern encryption technology has evolved far beyond the complex, business-disrupting systems of the past. Today’s encryption solutions work quietly in the background, protecting your data without slowing down your operations or frustrating your employees.
The beauty of working with experienced professionals is that you don’t need to become an encryption expert yourself. Our team handles the technical complexity while you focus on what you do best – running your business. Our 24/7 managed IT and cybersecurity services ensure your encryption systems stay current with evolving threats and changing compliance requirements.
Don’t let another day pass with your business data sitting unprotected. The cost of implementing robust encryption is a tiny fraction of what you’ll face if cybercriminals access your sensitive information. Every day you wait is another day your business remains vulnerable to attacks that could have been prevented.
Ready to give your business data the protection it deserves? Contact us today to discuss how we can implement comprehensive encryption solutions that fit your business perfectly. Our managed IT services include everything you need to keep your data secure, your compliance requirements met, and your peace of mind intact. Your business – and your customers – deserve nothing less than the strongest protection available.

